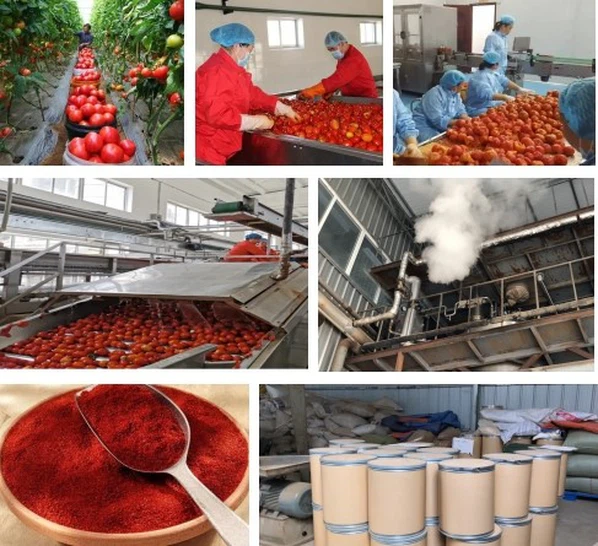
1. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress Capacity
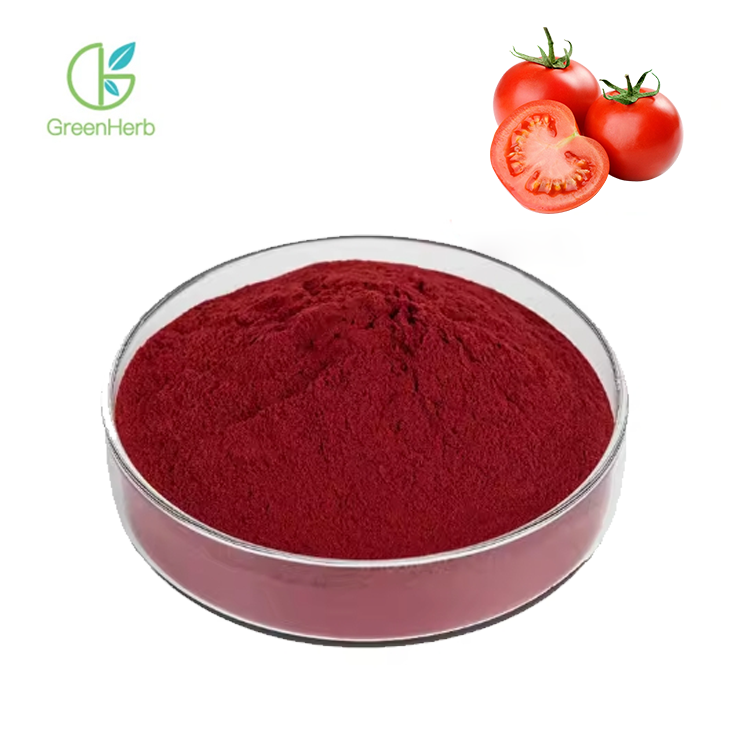
The long-chain polyunsaturated olefin structure of lycopene grants it a strong ability to neutralize free radicals and resist oxidation. Research highlights its key biological effects, including its potent antioxidant properties, potential in reducing cardiovascular disease risk, mitigating genetic damage, and inhibiting tumor development. Lycopene's in vitro antioxidant capacity has been confirmed through numerous studies. It is known to quench singlet oxygen more than twice as effectively as β-carotene and 100 times more effectively than vitamin E.
2. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Protection
Lycopene plays a significant role in protecting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems. It helps remove vascular debris, regulate plasma cholesterol levels, protect low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from oxidation, and repair oxidized cells. Additionally, it promotes the formation of intercellular glial cells and enhances vascular flexibility. Epidemiological studies indicate a negative correlation between serum lycopene levels and the incidence of cerebral infarction and hemorrhage. Experimental research on rabbits has shown that lycopene effectively reduces serum total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) to levels comparable to those achieved with fluvastatin sodium. Moreover, lycopene protects against local cerebral ischemia by inhibiting glial cell activity through its antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects, thereby reducing cerebral perfusion injury.
3. Skin Protection
Lycopene also offers protective benefits for the skin by reducing radiation and ultraviolet (UV) damage. When UV exposure occurs, lycopene in the skin binds to free radicals generated by UV radiation, thereby shielding skin tissues from harm. Compared to unexposed skin, lycopene levels in UV-exposed skin decrease by 31% to 46%, while other skin components remain relatively unchanged. Research indicates that consuming lycopene-rich foods can help combat UV radiation and prevent UV-induced redness. Additionally, lycopene can neutralize free radicals in epidermal cells, significantly reducing age-related pigmentation.
4. Immune System Enhancement
Lycopene contributes to immune system health by activating immune cells, protecting phagocytes from oxidative damage, promoting T and B lymphocyte proliferation, stimulating effector T cell function, and encouraging the production of certain interleukins while inhibiting inflammatory mediators. Studies have shown that moderate intake of lycopene supplements can enhance immune function and mitigate immune system damage caused by acute exercise.
 Protein Powder22 个产品
Protein Powder22 个产品  Freeze Dried Powder00 个产品
Freeze Dried Powder00 个产品  Fruit & Vegetable Juice Powder55 个产品
Fruit & Vegetable Juice Powder55 个产品  Amino Acid00 个产品
Amino Acid00 个产品  Ratio Extract Powder33 个产品
Ratio Extract Powder33 个产品  Red Clover Extract00 个产品
Red Clover Extract00 个产品  Standard Herb Extract1616 个产品
Standard Herb Extract1616 个产品  Natural Colourings00 个产品
Natural Colourings00 个产品  Active Ingredients Monomer11 个产品
Active Ingredients Monomer11 个产品